Mapping software serves a variety of purposes.
For educational settings, interactive maps enhance learning experiences, while urban navigation applications facilitate dynamic route planning.
Environmental monitoring tools can visualize data trends over time, proving invaluable for researchers and policymakers.
In the logistics and transportation sector, comprehensive mapping solutions support route optimization and efficiency in deliveries.
Catering to these needs, Google Earth has largely remained at the forefront of mapping software in the recent years. However, Google Earth is not the only tool in its category today.
Many users are turning to other tools that offer better experience and features.
This guide will highlight some of the best Google Earth alternatives, ensuring you find the right tool that suits your needs.
Let’s find out more.
Why Look for Alternatives to Google Earth?
Despite its powerful features, Google Earth has certain limitations. For eg:
Google Earth may not always provide precise geographical data. The elevation data, in particular, can have significant errors, which could affect projects requiring high accuracy, such as geodesic works or road surveys.
It also lacks real-time updates for certain data, such as traffic conditions, which may compromise its effectiveness for navigation and planning purposes.
While Google Earth can function offline, many of its features require a stable internet connection to access the latest satellite imagery and data. This can be a limitation in areas with poor connectivity.
In addition, some functionalities, especially in Google Earth Engine, require programming skills in languages like JavaScript or Python.
This can be a barrier for users without technical expertise, making it less accessible for non-programmers.
As with many Google services, there are concerns regarding data privacy and the potential misuse of location data. Users don’t like their data to be shared with third-parties.
Finally, the support for Google Earth and its advanced features is primarily in form of self-service, which may not assist users who encounter complex issues.
While there are community resources, direct support options are limited unless users opt for premium services.
All these reasons and more often necessitate users to look for alternative tools.
Best Google Earth Alternatives
1. Zoom Earth
Zoom Earth is a powerful Google Earth alternative that provides excellent imagery, real-time data, historical views, and a user-friendly interface.
Here are some key points about Zoom Earth:
High-Quality Aerial Imagery – Zoom Earth provides high-resolution satellite imagery for detailed views of various locations around the world. The image quality is often better than what Google Earth offers.
Real-Time Earth Simulation – Zoom Earth shows real-time information about weather, storms, wildfires and more. It uses data from NOAA, NASA, Japan’s and EU’s satellites to simulate the Earth in real-time.
Historical Imagery – Just like Google Earth, Zoom Earth allows you to view historical satellite imagery dating back to the mid-1990s. You can track changes to locations over time.
Offline Capabilities – Zoom Earth is web-based, so it requires an internet connection to use. However, it works well on mobile devices and tablets.
Open Data Sources – Zoom Earth integrates with OpenStreetMap and other open data sources, providing users with a customizable interface and data visualization options.
Ease of Use – With basic controls and intuitive features like zooming in and out, Zoom Earth makes it easy to explore the world and find your desired destination.
Overall, Zoom Earth is a great choice for casual exploration and visualization of the Earth.
2. NASA WorldView
NASA Worldview is a web-based mapping application that provides users with access to real-time satellite imagery and data.
It is particularly valuable for monitoring environmental changes and natural disasters, offering a range of features that set it apart from other mapping tools, including Google Earth.
Take a look at its key features:
- Real-Time Satellite Imagery: NASA Worldview allows users to view live satellite data, with updates available within three to four hours of observation. This feature is crucial for applications such as wildfire management and air quality monitoring.
- Extensive Data Layers: The platform offers over 800 global, full-resolution satellite imagery layers, which can be explored interactively. Users can add layers based on specific science disciplines or natural hazards.
- Timelapse and Animation Capabilities: Users can create animations and timelapse videos to visualize changes over time, making it easier to understand dynamic environmental processes.
- User-Friendly Interface: The application supports familiar mapping interactions, allowing users to pan, zoom, and select imagery easily. It also includes options for customizing image resolution and file formats for downloads
- Snapshot Tool: For users who do not require interactive features, Worldview Snapshots enables the creation and downloading of static images quickly.
- Global Coverage: The platform provides a comprehensive view of the Earth, including polar stereographic views for the Arctic and Antarctic regions, which enhances its usability for global monitoring.
NASA Worldview is a powerful tool for accessing real-time satellite imagery and environmental data, making it a valuable resource for specific applications, especially when compared to Google Earth’s historical focus.
3. ArcGIS Earth
ArcGIS Earth is another Google Earth alternative.
It is a 3D geospatial visualization tool developed by Esri, designed to provide users with an intuitive interface for exploring, analyzing, and sharing geographic data.
ArcGIS Earth is part of the ArcGIS suite of applications and serves as a lightweight alternative to more complex GIS software like ArcGIS Pro.
Here are some features of ArcGIS Earth:
- 3D Visualization: ArcGIS Earth allows users to visualize geospatial data in a 3D environment, enabling a more immersive exploration of geographic features.
- Data Integration: Users can connect to ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise to access a variety of basemaps and datasets. It supports multiple data formats, including KML, CSV, GeoJSON, and 3D Tiles, allowing for versatile data integration.
- Editing Capabilities: The software supports direct editing of feature services, enabling users to modify attributes and geometry of geospatial features. The feature is particularly useful for collaborative projects and data updates.
- Interactive Analysis Tools: ArcGIS Earth includes tools for measuring distances, analyzing line of sight, and creating viewsheds, which assist users in conducting spatial analyses directly within the application.
- Bookmark and Tour Creation: Users can create and share bookmarks and tours, which can include geotagged photos, enhancing storytelling and presentation of geographic information.
- User-Friendly Interface: The application features a streamlined interface that is accessible to both professional GIS users and newcomers, making it easier to navigate and utilize its functionalities.
- Mobile Compatibility: ArcGIS Earth is also available on mobile platforms, allowing users to access and interact with geospatial data on the go.
- Customizability: Users can personalize tool preferences and settings, enhancing their workflow and user experience.
While Google Earth is designed for general users and casual exploration, ArcGIS Earth is tailored for professionals and organizations that require more robust geospatial analysis and data editing capabilities.
4. OpenStreetMap
OpenStreetMap is a collaborative mapping project that allows users to create, edit, and use map data freely.
It operates under an open-content license, making it accessible for various applications without the restrictions typical of commercial services like Google Maps.
The platform has a vast community of contributors, which helps maintain and update the map data regularly, often resulting in more localized and detailed information in areas where commercial mapping services may be lacking.
Here are the key features of OpenStreetMap:
- Free and Open Data: OSM provides complete access to its datasets, allowing users to download and use map data offline. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring extensive geospatial analysis or routing capabilities without incurring costs associated with API usage limits found in Google Maps.
- Community-Driven Updates: The data in OSM is continuously updated by volunteers, which can lead to quicker updates in local areas compared to the slower moderation processes of Google Maps. The community aspect often results in more accurate and timely information in specific regions.
- Customization and Flexibility: OSM allows developers to customize maps extensively. Users can create tailored maps that meet specific needs, which is not as easily achievable with Google Maps due to its proprietary nature.
- Routing and Navigation: While OSM does not provide built-in routing and navigation features like Google Maps, it supports third-party tools that can integrate these functionalities. The flexibility allows for the development of specialized routing applications, such as those focusing on cycling or hiking routes.
- Diverse Applications: Beyond traditional mapping, OSM data is utilized in various applications, including urban planning, disaster response, and logistics, making it versatile for different industries.
OpenStreetMap is a robust alternative to Google Earth, particularly for users and developers who value open data, customization, and community-driven content.
Its strengths lie in its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to access detailed local information.
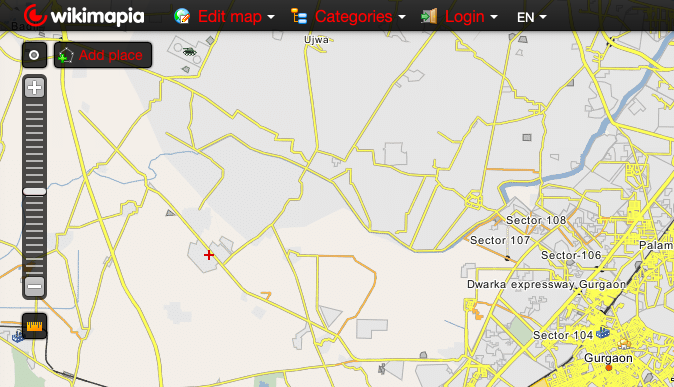
5. Wikimapia
Wikimapia is a community-driven mapping tool that allows users to add and edit information about locations. While it may not be as feature-rich as Google Earth, it offers a unique collaborative approach to mapping.
Here’s what you get with Wikimapia:
- Interactive Map: Wikimapia provides a Google Maps-based interactive map with scroll and zoom functionality, allowing users to navigate and explore locations.
- User-Generated Content: Wikimapia is a crowdsourced platform where users can add, edit, and describe geographical objects like buildings, forests, and streets. The user-generated descriptions and tags provide additional context to the map.
- Multilingual Support: It also supports multiple languages, and the descriptions of objects can be added in different languages.
- Embedded Maps: The Wikimapia maps can be embedded on other websites, making it easy to share and integrate the maps into other projects.
- Mobile Apps: The tool is available as mobile apps for iOS and Android devices, allowing users to access the maps on the go.
- Measuring Tools: Wikimapia provides tools for measuring distances between objects and refining existing places according to categories.
The choice between Wikimapia and Google Earth ultimately depends on the user’s specific needs and preferences.
Wikimapia is more suitable for those who want to contribute to and explore user-generated content, while Google Earth is better suited for those who prioritize advanced visualization features and high-quality satellite data.
6. OssimPlanet
OssimPlanet is a viable alternative to Google Earth, particularly for users seeking a robust 3D global visualization system.
It is built on open-source software libraries, including OSSIM, OpenSceneGraph, and Trolltech QT, which allows it to offer a range of features that cater to both casual users and professionals in geospatial fields.
There are several features OssimPlanet offer such as –
- 3D Global Visualization: OssimPlanet provides accurate 3D visualization of geo-spatial data, making it suitable for various applications, including environmental monitoring and urban planning.
- Data Format Support: It supports a wide array of commercial and government data formats, which enhances its usability for different types of geospatial data analysis. Users can access native file formats, GDAL formats, and even OGC WMS (Web Map Service) and WorldWind servers, allowing for extensive data integration and visualization capabilities.
- Collaboration Capabilities: OssimPlanet allows for distributed collaboration, where multiple instances can be synchronized to work together. This feature is particularly useful for teams working on large-scale projects or in research environments.
- Customization and Extensibility: Users can customize their experience by integrating various data layers, including elevation models and satellite imagery. The software can fetch data from remote servers, enhancing its functionality and keeping the information up-to-date.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: OssimPlanet is available on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, which broadens its accessibility to different user bases.
OssimPlanet serves as a powerful substitute to Google Earth, especially for users in professional settings requiring detailed geospatial analysis and collaboration tools.
7. Biosphere3D
Biosphere3D is an open-source landscape visualization system designed to handle planet-sized terrains.
It is being developed as a potential alternative to Google Earth, focusing on realistic scene rendering and advanced terrain management capabilities. Here are its key features.
- Open Source: Biosphere3D is released under the Mozilla Public License (MPL), making it accessible for modification and redistribution.
- Terrain Management: It uses a sophisticated terrain management and rendering system, capable of handling large satellite images and digital elevation models, with testing conducted on datasets up to 2TB uncompressed.
- Basic GIS Support: The software includes basic support for Geographic Information System (GIS) data, allowing users to overlay shape files on the terrain.
- Platform Availability: Currently, it is available for Windows (both 32 and 64-bit versions), with some components being posix compatible, although the project lacks extensive contributions from the community.
- Vegetation Rendering: The primary focus of Biosphere3D is on rendering vegetation, which sets it apart from other visualization tools.
- Research Background: The development team has published research on the system at conferences such as EuroVis and SimVis, indicating a foundation in academic research.
Biosphere3D’s capabilities are still developing, particularly in areas like virtual globe functionalities, KML support, and community engagement.
8. Marble
Another reliable alternative to Google Earth, particularly for Linux users is Marble.
Marble is an open-source virtual globe and world atlas developed by the KDE community.
It offers a variety of features that cater to both casual users and those interested in more detailed geographic information.
Marble is known for offering excellent features including:
- Multiple Map Views: Marble provides various map views, including topographic, satellite, and historical maps. Users can switch between at least 15 different views, such as OpenStreetMap and a satellite view based on NASA imagery, as well as historical maps dating back to the 17th century.
- Routing and Navigation: The application includes advanced routing capabilities for different modes of transportation (driving, walking, cycling) and allows users to set waypoints along their routes. It can also integrate with GPS devices to track real-time locations.
- Customization: Marble is highly customizable, supporting numerous plugins and settings. Users can modify the interface and functionality to suit their preferences, including the ability to download additional map views.
- Educational Use: With its historical maps and various educational features, Marble is particularly useful for teaching geography. The application allows users to visualize changes over time and explore different geographic perspectives.
- Integration with Online Services: Marble can pull in data from various online sources, including weather reports and Wikipedia articles, enhancing the informational depth of the maps.
- Lightweight Performance: Unlike Google Earth, which can be resource-intensive, Marble is designed to run efficiently on lower-powered systems, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
- Privacy-Focused: Marble is an open-source project, which means it does not have the same privacy concerns associated with proprietary software like Google Earth. The aspect appeals to users who prioritize data privacy.
While Google Earth is well-known for its polished interface and extensive imagery, Marble offers a more modular and customizable experience.
9. NASA World Wind
NASA World Wind is an open-source virtual globe API that allows developers to create interactive 3D visualizations of geographic information.
Initially released in 2003, it has since evolved into a versatile platform for various applications, including weather monitoring, urban planning, and educational tools.
Here are some of its notable features:
- Open Source: NASA World Wind is completely open-source, which facilitates easy extension and customization of its capabilities.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: It operates on multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices, with implementations in Java, JavaScript, and Android.
- SDK for Developers: Unlike consumer-oriented applications like Google Earth, World Wind serves as a software development kit (SDK), providing developers with the tools to build their own applications around the virtual globe.
- 3D Geographic Visualization: The API allows for the display of high-resolution imagery and terrain data from various sources, enabling users to visualize complex geographic information in three dimensions.
- Multiple Planetary Models: World Wind includes models for Earth, Mars, and the Moon, allowing for diverse applications in planetary science and exploration.
- Rich Graphics Features: It supports various geometric shapes and annotations, including paths, polygons, and 3D objects, which can be used to represent geographic data interactively.
- Wide Range of Data Formats: World Wind can handle multiple data formats, including KML, GeoJSON, and various imagery formats like JPEG and GeoTIFF. The flexibility allows integration with numerous geospatial data sources.
- Automatic Data Retrieval: The platform can automatically retrieve and cache geographic data from remote servers, optimizing performance and user experience.
- User Interaction: Developers can implement interactive tools for users to manipulate the globe, such as zooming, rotating, and selecting specific data points.
- Web Integration: The Web World Wind version allows for embedding the globe in web applications, providing a JavaScript API for extensive customization and control over visualization.
The platform is widely used in educational settings and research as well, fostering collaboration among scientists and developers.
Its modular architecture supports various educational tools, enhancing understanding of Earth’s dynamics and geospatial analysis.
10. Here WeGo
Here WeGo is a free navigation app developed by HERE Technologies that can serve as an alternative to Google Earth for certain use cases.
While it may not have the same level of detail and features as Google Earth, Here WeGo offers a user-friendly interface and solid navigation capabilities.
The mapping service provides various features suitable for both local navigation and broader travel needs. Here are a few of them:
- Offline Maps: One of the standout features of Here WeGo is its ability to download maps for entire countries or continents, allowing users to navigate without an internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for travelers who may encounter areas with poor reception.
- Turn-by-Turn Navigation: Here WeGo offers voice-guided navigation and turn-by-turn directions, similar to Google Maps. It allows users to choose their preferred route and provides real-time traffic updates.
- Public Transport Information: The app includes information on public transport, showing local buses and their schedules, which is updated in real time. This feature is useful for users relying on public transportation.
- User-Friendly Interface: Here WeGo boasts a clean and intuitive design, making it easy for users to search for locations and access navigation options.
- Points of Interest: While it provides information on various points of interest, such as restaurants and tourist attractions, it may not have as extensive a database as Google Maps.
- Route Customization: Users can customize their routes based on preferences, such as avoiding tolls or selecting the fastest route, which enhances the navigation experience.
- Cross-Platform Availability: Here WeGo is available on multiple platforms, including iOS and Android, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
While Here WeGo may not offer the same level of detailed satellite imagery or 3D terrain visualization as Google Earth, it serves as a robust navigation tool with unique features that cater to users looking for offline capabilities and public transport information.
Wrap Up
While Google Earth remains a robust tool for virtual exploration, its limitations in navigation, collaboration, and offline use prompt users to consider alternatives.
Options like ArcGIS Earth and Zoom Earth provide specialized features that can better meet the needs of professionals in various fields.
Feel free to use them if Google Earth fails to meet your expectations.